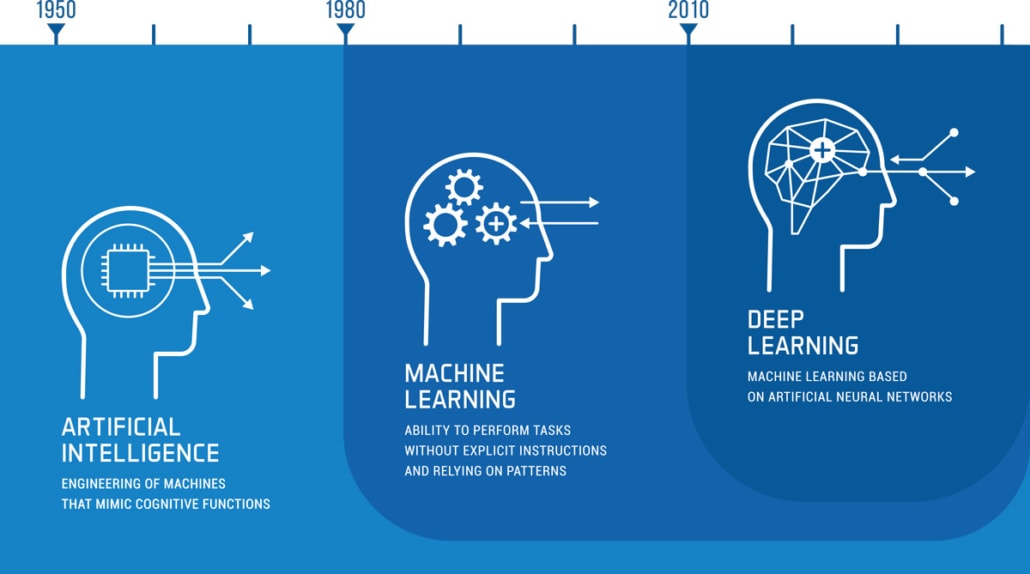
Technology as an engine of change: This is what AI in software engineering is changing in organization and collaboration
In the first part of this article we gave an overview of AI tools and their potential impact in the field of software engineering. In this part we look at the effects on organizations and how people work together.
The key to good team collaboration will lie in flexibility, a willingness to learn and and a heavier focus on innovation and customer satisfaction. Those companies which best manage those changes will become more competitive and will be in a position to make optimal use of the opportunities afforded by the AI revolution.
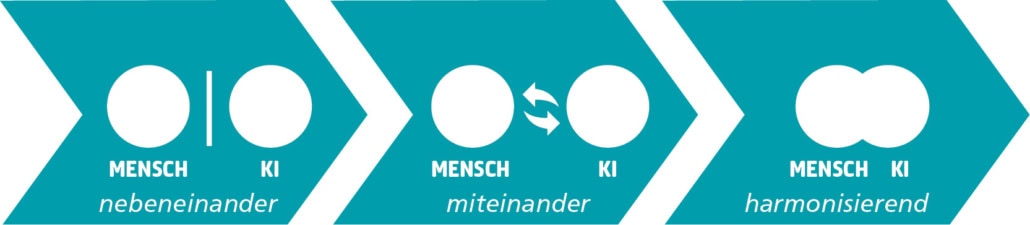
Integration of AI in work processes
Teams will be working increasingly with AI systems so they can handle tasks more efficiently. This in turn will necessitate that the development process be adapted so it can integrate AI. Developers will use AI systems as tools for support, and learn how they can best profit from them. Man-machine collaboration is becoming the norm.
Development of agile skills
Employees will need to be more flexible and have the ability to quickly adapt to new technologies and tools, since AI systems and technologies continue to undergo rapid, dynamic development. And in order to use AI effectively, employees may need to acquire skills and know-how in new sectors, whether this be machine learning, data analysis or tools for AI development.
Changes in roles and tasks
Organizations are seeing the birth of new roles based on AI specializations, such as AI architects, data scientists and AI ethics officers. At the same time certain tasks, such as writing code and testing software, which up to now were performed by humans are becoming increasingly automated, and (as in previous digitalization waves) employees are gradually focusing on more complex tasks. As a result, another central task necessary to address the AI wave of change is the continued development of existing personnel to expand their skill sets.
Ethics and governance
An organization which makes use of artificial intelligence (AI) must develop clear guidelines on the related ethics and governance. These guidelines are crucial in ensuring that an organization’s use of AI reflects its values as well as the interests of all relevant interest groups – a few keywords which come to mind in this regard include transparency, data protection, fairness and security. In addition, compliance with ethical and legal standards should be monitored and employees trained accordingly. Finally, transparent communication with customers on the organization’s use of AI is also essential.
Knowledge building and knowledge transfer
Organizations must share and disseminate knowledge on how to use AI effectively in order to ensure that all employees can profit from the new technologies. The employees in an organization must develop at least a basic understanding of AI technologies, including familiarity with the different forms of AI, their areas of application and how they work. In addition, the use of AI within an organization requires specific domain knowledge on the company’s business processes and goals. This is essential for identifying relevant data, validating models and integrating results into the company’s business strategy.
Furthermore, organizations must invest in building up their data expertise. This includes the collection, cleansing and organization of data sources for the purpose of creating high-quality data set for AI applications. Finally, continuous training and adapting to changes are also extremely important since AI technologies are constantly undergoing further development, and both employees as well as organizations as a whole must keep up-to-date. This requires training, exchanges of best practices and a willingness to integrate new findings and technologies into company workflows.
Cultural change
Implementing AI often necessitates a cultural change to which employees must be open and also willing to accept new ideas and technologies to make the transformation a successful one. And in the face of technological innovation which is constantly accelerating, organizations must also open up and make better use of their existing potential.
Agile organizations respond to this change more quickly, and are better able to turn trends to their advantage. By contrast, hierarchical organizations are faced with the challenge that agile methods are accompanied by a change in mindset and culture, which radically changes existing approaches of collaboration and decision-making.
Customer orientation and customer relationships
Companies will use AI to better adapt their software to the needs of their customers and to interact with them more directly. These goals will necessitate stronger customer orientation as well as the ability to integrate customer feedback into product development.
TAKEAWAY: THE OPPORTUNITY TO USE AI
Integrating AI into the software development process offers countless advantages, from automating routine tasks to customizing advanced training programs for developers.
Nevertheless, it’s important to stress that AI should not be seen as a replacement for human specialist knowledge and intuition, but more as a tool which supports software developers in their work. By combining human creativity with the performance capabilities of AI, we can usher in a new era of software engineering which is more productive, efficient and innovative than ever before.